The Indian government is moving towards making Vehicle-to-Vehicle (V2V) communication technology mandatory in cars, a step aimed at significantly improving road safety across the country. The announcement was made by Union Road Transport and Highways Minister Nitin Gadkari on January 9, 2026, underlining the government’s push to reduce accidents through advanced automotive technology.
What Is V2V Technology and How “Talking Cars” Work
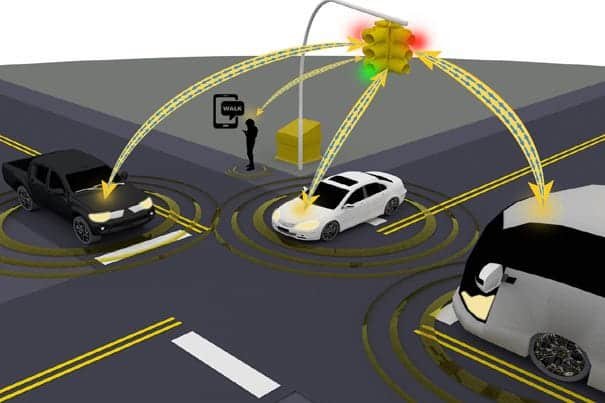
V2V technology enables vehicles to communicate wirelessly with each other in real time. Cars equipped with this system can send and receive safety-related information such as sudden braking, emergency stops, lane changes, or the presence of vehicles in blind spots.
This real-time exchange allows drivers to receive early warnings about potential dangers, even before they become visible on the road. The system works automatically in the background, assisting drivers without requiring manual input.
Why the Government Is Making V2V Mandatory
India continues to record a high number of road accidents and fatalities, largely due to delayed driver reaction, overspeeding, and lack of situational awareness. According to the government, technology like V2V can directly address these issues by giving drivers extra seconds to react.
The mandate is part of a broader national strategy to cut road deaths by 50 percent by 2030, shifting the focus from reactive enforcement to preventive, technology-driven safety solutions.
How V2V Can Reduce Accidents on Indian Roads

V2V systems are designed to improve safety in high-risk situations, including:
- Sudden braking by vehicles ahead
- Congested traffic conditions
- Highway overtakes and blind curves
- Poor visibility due to fog, rain, or night driving
By alerting drivers in advance, V2V technology can help prevent rear-end collisions, side-impact crashes, and multi-vehicle pileups.
Implementation Plan for New Vehicles
The proposed mandate is expected to apply primarily to new vehicles sold in India, with onboard communication units becoming a standard safety feature over time. These systems will operate on dedicated automotive communication spectrum, ensuring reliable and low-latency data transfer between nearby vehicles.
The government is expected to finalise technical standards and timelines after consultations with automakers, suppliers, and regulatory bodies.
Role of the Transport Ministry and Safety Laws
Road safety initiatives are being led by the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways, which is also working on parallel measures such as safer highway design, faster emergency response, and stricter vehicle safety norms.
Reforms under the Motor Vehicles Act continue to play a key role in supporting technology adoption and improving compliance across states.
Preparing India for the Future of Connected Mobility
Experts believe that mandatory V2V adoption will help India lay the foundation for connected and autonomous mobility ecosystems. While fully autonomous vehicles may still be years away, V2V technology is seen as a practical and immediate step that delivers real-world safety benefits today.
Once implemented, the mandate could mark one of the most significant safety upgrades in India’s automotive sector, aligning the country with global best practices in connected vehicle technolog